Ultracompact polarization-entangled photon sources for miniaturized quantum devices
USA, August 27, 2024 /EINPresswire.com/ -- Scientists created a new ultra-thin source of entangled photons, a key component for future quantum technologies. This new source uses a special material called rhombohedral tungsten disulfide, which offers high quality and efficiency. It could pave the way for miniaturized devices in quantum information processing.
Scientists have created a groundbreaking ultra-thin light source that emits pairs of polarization-entangled photons. These specially correlated photons hold immense promise for future quantum technologies, including ultra-secure communication, powerful computation, and high-precision measurements. This light source is particularly small, pure, efficient, and versatile.
Entangled photons share a unique connection. By measuring one photon's properties, scientists can instantly determine the properties of its entangled partner, regardless of distance. This phenomenon has the potential to revolutionize fields like communication, computation and metrology.
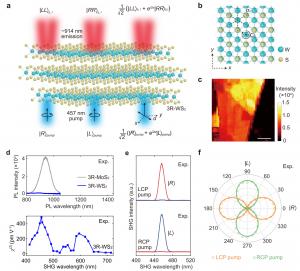
The new light source is made from a special material called 3R-WS2 and is hundreds of times thinner than a human hair. This material allows the light source to be miniaturized and integrated into future quantum photonic circuits.
The researchers achieved this breakthrough by carefully selecting a material with the right properties. The material needs to be able to efficiently generate entangled photons and have a well-defined internal structure. The researchers have identified the rule of material selection for polarization entanglement, facilitating the search for other potential quantum materials with superior performance.
This research represents a significant step forward in developing practical quantum technologies. By creating smaller, more efficient sources of entangled photons, scientists are bringing quantum technology closer to reality.
DOI
10.1186/s43593-024-00074-6
Original Source URL
https://doi.org/10.1186/s43593-024-00074-6
Funding information
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2022YFA1204704), the Innovation Program for Quantum Science and Technology (2021ZD0303200, 2021ZD0301500), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (62061160487, T2325022, U23A2074, 62205325), the CAS Project for Young Scientists in Basic Research (No. YSBR-049), Key Research and Development Program of Anhui Province (2022b1302007), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, the NRF, Prime Minister’s Office, Singapore under the Competitive Research Program Award (Grants No. NRF-CRP26-2021-0004), A*STAR SERC MTC Programmatic Funds under grant number M23M2b0056, NRF-CRP22-2019-0006 and NRFCRP26-2021-0063).
Lucy Wang
BioDesign Research
email us here
Legal Disclaimer:
EIN Presswire provides this news content "as is" without warranty of any kind. We do not accept any responsibility or liability for the accuracy, content, images, videos, licenses, completeness, legality, or reliability of the information contained in this article. If you have any complaints or copyright issues related to this article, kindly contact the author above.