Innovative methods for removing radioactive cesium from wastewater in the context of nuclear disasters
CHINA, January 17, 2024 /EINPresswire.com/ -- Radioactive wastewater is an unavoidable byproduct of nuclear operations, containing harmful radionuclides like cesium, which pose serious health risks. The Fukushima Daiichi nuclear accident highlighted the urgency of effectively removing radioactive cesium from wastewater. This review provides a comprehensive analysis of current methods and technologies for cesium removal, with a focus on the aftermath of the Fukushima incident.
In a recent comprehensive review published in Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering on 05 December 2023, researchers from Tsinghua University delves into the various innovative methods in the removal of radioactive cesium from wastewater.
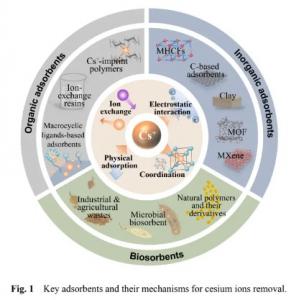
Researchers assesses several adsorption and membrane separation techniques used in cesium removal in this review. They explore a range of adsorbents, categorizing them into inorganic, organic, and biological materials, and evaluates their efficacy in capturing cesium ions. They also discuss membrane-based separation methods, including reverse osmosis, forward osmosis, and membrane distillation, highlighting their roles in cesium ion separation. Special attention is given to the methods employed in the cleanup efforts following the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear accident, notably the Kurion/SARRY system, the desalination system, and the Advanced Liquid Processing System (ALPS). Given cesium's unique properties, such as its small hydrated radius and high diffusion coefficient, these methods face significant challenges in effectively isolating cesium ions from water.
Professor Jianlong Wang, the corresponding author of this review, comments, "The task of removing radioactive cesium from wastewater is not just a scientific challenge but a necessity for maintaining ecological balance and public health. The advancements in adsorption and membrane separation technologies represent significant steps forward, yet continuous innovation is essential."
The review concludes that the removal of radioactive cesium is a complex but vital undertaking. Adsorption emerges as a highly effective method for managing low concentrations of radionuclides in large volumes of wastewater, with certain materials showing exceptional adsorption capacity and selectivity. Membrane separation technologies like reverse osmosis also play a crucial role, especially evidenced in the Fukushima cleanup. Despite the progress, the review underscores the need for further advancements, particularly in addressing challenges like the treatment of concentrated retention liquid and enhancing the radiation stability of membrane materials. The findings underscore the importance of these technologies in protecting the environment and public health from the hazards of nuclear activities.
DOI
10.1007/s11783-024-1798-1
Original Source URL
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-024-1798-1
Funding information
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 515783307) and the National Key Research and Development Program (No. 2016YFC1402507).
Lucy Wang
BioDesign Research
email us here
Legal Disclaimer:
EIN Presswire provides this news content "as is" without warranty of any kind. We do not accept any responsibility or liability for the accuracy, content, images, videos, licenses, completeness, legality, or reliability of the information contained in this article. If you have any complaints or copyright issues related to this article, kindly contact the author above.