Mapping the Genetic and Therapeutic Landscape of Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer
SHANNON, CLARE, IRELAND, April 20, 2025 /EINPresswire.com/ --
Anaplastic thyroid cancer (ATC), a rare yet highly aggressive malignancy, continues to represent a major clinical challenge. A recent review published in Genes & Diseases offers a comprehensive overview of the molecular mechanisms, diagnostic approaches, and therapeutic strategies driving current and future management of this lethal disease. ATC, accounting for a small percentage of thyroid cancers, progresses rapidly and resists conventional therapies, underscoring the urgency for innovative treatment paradigms.
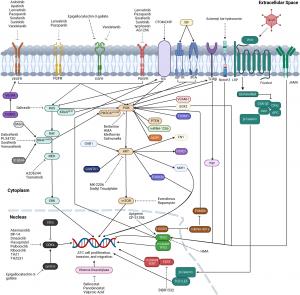
At the core of ATC’s pathogenesis are genetic aberrations, with prominent alterations in MAPK and PI3K-AKT-mTOR signaling pathways. These dysregulated pathways promote unchecked cellular proliferation, survival, and metastasis. Mutations in genes such as BRAF, RAS, PIK3CA, TP53, and TERT have emerged as key drivers of ATC development and progression. Understanding the interplay between these mutations has enabled refined subclassifications of ATC, potentially informing personalized therapeutic approaches.
The review emphasizes the significance of targeted therapies, especially BRAF and MEK inhibitors, in improving patient outcomes. In particular, dual inhibition strategies have demonstrated efficacy in shrinking tumors and enabling surgical interventions. While trimodal therapy—a combination of surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation—remains the cornerstone for localized disease, its limitations in advanced ATC highlight the need for additional therapeutic avenues.
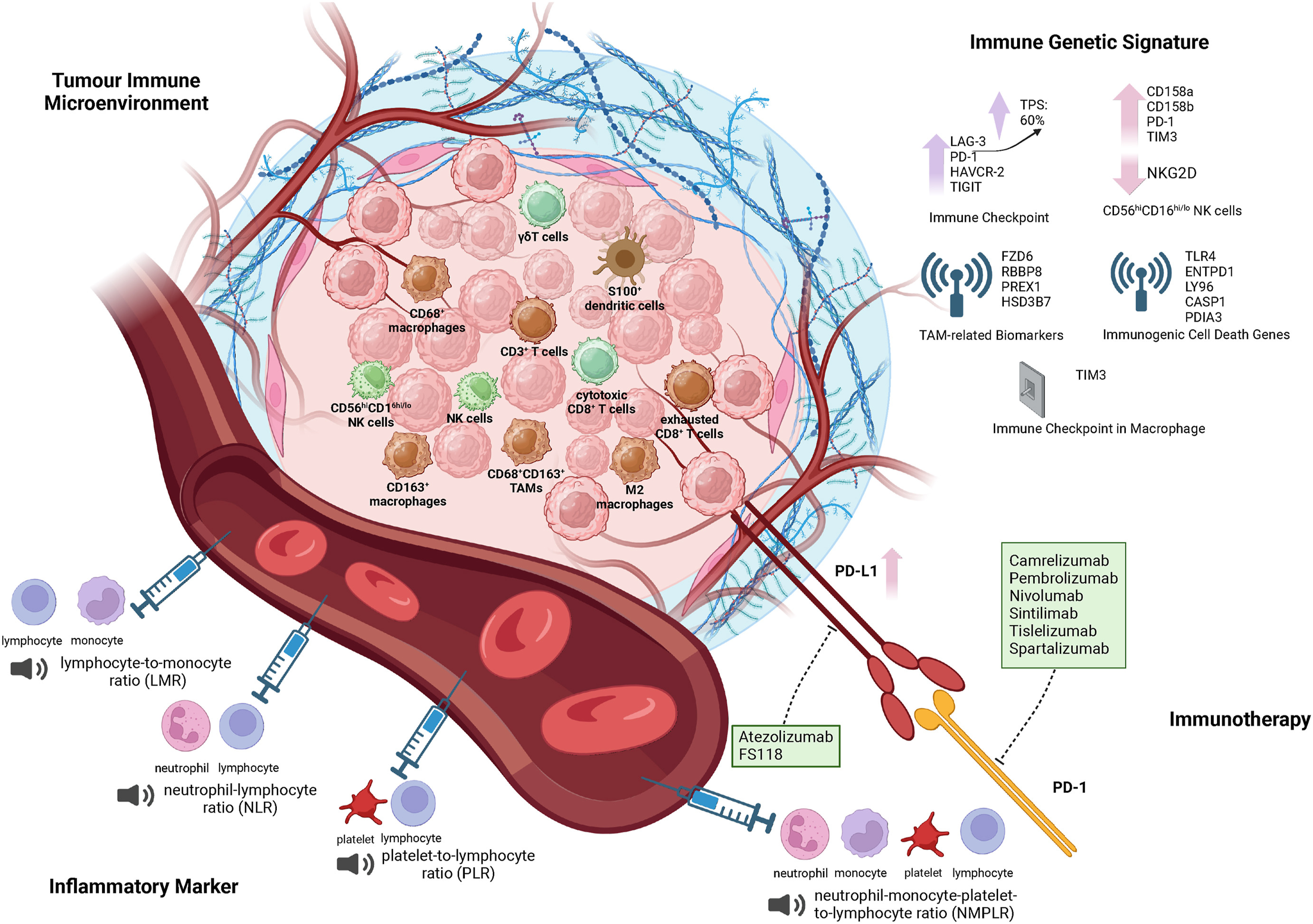
Immunotherapy has gained traction as a complementary modality. The tumor microenvironment of ATC, marked by immune cell infiltration and PD-L1 overexpression, presents opportunities for immune checkpoint inhibitors. However, response rates remain variable, and research is ongoing to optimize patient selection and treatment combinations.
Diagnostic innovations are also covered in detail, including the comparative efficacy of fine needle aspiration (FNA) versus core needle biopsy (CNB) and the utility of 18F-FDG PET/CT imaging in staging and treatment planning. Advances in immunohistochemical markers and liquid biopsies hold promise for earlier detection and real-time monitoring of therapeutic response.
The article concludes by highlighting the emerging role of mitochondrial metabolism as a therapeutic target and the potential of novel agents, including nanoparticles and oncolytic viruses, to enhance radioiodine uptake and overcome therapeutic resistance.
# # # # #
Genes & Diseases publishes rigorously peer-reviewed and high quality original articles and authoritative reviews that focus on the molecular bases of human diseases. Emphasis is placed on hypothesis-driven, mechanistic studies relevant to pathogenesis and/or experimental therapeutics of human diseases. The journal has worldwide authorship, and a broad scope in basic and translational biomedical research of molecular biology, molecular genetics, and cell biology, including but not limited to cell proliferation and apoptosis, signal transduction, stem cell biology, developmental biology, gene regulation and epigenetics, cancer biology, immunity and infection, neuroscience, disease-specific animal models, gene and cell-based therapies, and regenerative medicine.
Scopus CiteScore: 7.3
Impact Factor: 6.9
# # # # # #
More information: https://www.keaipublishing.com/en/journals/genes-and-diseases/
Editorial Board: https://www.keaipublishing.com/en/journals/genes-and-diseases/editorial-board/
All issues and articles in press are available online in ScienceDirect (https://www.sciencedirect.com/journal/genes-and-diseases ).
Submissions to Genes & Disease may be made using Editorial Manager (https://www.editorialmanager.com/gendis/default.aspx ).
Print ISSN: 2352-4820
eISSN: 2352-3042
CN: 50-1221/R
Contact Us: editor@genesndiseases.com
X (formerly Twitter): @GenesNDiseases (https://x.com/GenesNDiseases )
# # # # # #
Reference
Zhao Zou, Linhong Zhong, Anaplastic thyroid cancer: Genetic roles, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy, Genes & Diseases, Volume 12, Issue 4, 2025, 101403, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gendis.2024.101403
Genes & Diseases Editorial Office
Genes & Diseases
+86 23 6571 4691
editor@genesndiseases.com
Legal Disclaimer:
EIN Presswire provides this news content "as is" without warranty of any kind. We do not accept any responsibility or liability for the accuracy, content, images, videos, licenses, completeness, legality, or reliability of the information contained in this article. If you have any complaints or copyright issues related to this article, kindly contact the author above.